4/5/11 Meet the Wind Developer AND Why is that Canadian little old lady so angry about wind turbines?
THE ANGER IS BLOWING IN THE WIND
SOURCE: The London Free Press, www.lfpress.com
April 2, 2011
By Randy Richmond,
Grey-haired, 81-year-old Stephana Johnston is the kind of person to give the provincial Liberals fits when she waits outside Dalton McGuinty’s campaign bus this fall.
Leaning against her walker, she looks frail — except when she starts talking about wind power.
“We are suffering and it is a horror story and you are responsible because you agreed to the Green Energy Act,” Johnston tells Lambton-Kent-Middlesex Liberal MPP Maria Van Bommel.
With the next Ontario election only five months away, wind energy and the Green Energy Act is on track to become a huge issue of the campaign.
Johnston says she had to move from her home on the north shore of Lake Erie near Long Point after nearby wind turbines started interrupting her sleep.
“There are some nights when I wake up and just everything inside me is quivering. It has compromised my immune system. I am going everywhere I can go to prevent what has happened to us,” she vows.
Slowed by her walker but energized by her anger, Johnston still marched down the main street of Strathroy Saturday with about 80 others to protest wind turbines.
The peaceful protest march erupted into a raucous, hour-long confrontation with Van Bommel.
Van Bommel could barely finish a sentence without being shouted down by furious protesters who demanded she support a moratorium on turbines until research proves they are safe.
At times she had to stop and simply take the barrage of insults from protesters, some in tears and some claiming she betrayed their friendship.
“Imagine when (McGuinty’s) bus is met 28 days straight with crowds like that in Strathroy,” says John Laforet, president of Wind Concerns Ontario.
Urban dwellers and political analysts are underestimating the anger in rural and small town Ontario over wind turbines, he says. “This is the fight for the life and death of rural life. There is a huge anger out there and I think it is going to get worse.”
For wind energy opponents, the stakes are high. “This is our only shot,” Laforet says.
Wind Concerns — a coalition of 57 groups — will likely endorse either parties or individual candidates and encourage rural residents unhappy with McGuinty to work on getting him ousted.
Eighty municipalities representing two million people have called for a moratorium on wind farms, Laforet adds.
“There a lot of people looking for something to do. Direct political action is the most effective thing a resident of Ontario with concerns about wind can do.”
Hundreds of wind turbines have been installed or proposed in many areas of Southwestern Ontario, a 10-riding region dominated by McGuinty’s Liberals.
Opponents say turbines emit low-pitched sounds that disrupt the body’s rhythms and cause headaches, tinnitus, dizziness, nausea, rapid heart rate irritability and concentration problems.
Proponents say there is no proof of ill effects and turbines are better for the environment and personal health than the coal-fired generating plants they are supposed to replace.
“It’s a very emotional issue and I think we have to recognize that,” Van Bommel said Saturday after the protest. “There are many things that are going to be election issues in rural Ontario. I‘m sure the Green Energy Act will be uppermost in many people’s minds.”
4/3/11 It was yours but they broke it, can't fix it, and say Too bad take it or leave it, AND Our money or your (wild) life: Wind lobbyists say protecting wildlife is too expensive and will delay wind projects AND What looks like a tornado to the National Weather Service, looks like a plane to the military, and looks like big money to wind developers and guess whose interests matter most?
WIND FIRM MAKES FINAL OFFER
SOURCE: Renewablesbiz.com
March 31, 2011
By David Giulliani
A wind company has made its "last and final offer" to residents complaining about problems with their TV reception, which they blame on nearby turbines.
Big Sky Wind, a subsidiary of Edison Mission Group, has a wind farm with turbines in Lee and Bureau counties.
Bureau County residents near the turbines have been particularly vocal about TV reception and noise problems. They also have complained about shadow flicker, which are the shadows of rotating blades that pass over windows that experts say cause seizures in some people.
Last week, Big Sky sent letters via Federal Express to residents who have complained about the problems.
In the letter, the company stated it had offered a settlement of $2,500 for each resident to resolve their TV reception complaints.
"We believe this to be a fair market offer that has already been accepted by several of your neighbors," the letter says. "With this in mind, we consider the $2,500 to be our best, last and final offer to resolve your TV reception complaint."
In the letter, Big Sky said it understands that residents also have complaints about noise and flicker. The company said it's prepared to offer a fair monetary settlement to resolve those issues, as well.
To start those settlement discussions, Big Sky requires that residents sign confidentiality agreements already sent out. The company asks that those agreements be faxed to its attorney in California.
Big Sky spokesman Charley Parnell said the letter and confidentiality agreement are intended to jump-start settlement discussions. He said most of the complaints his firm has received have come from Bureau County, but a few have come from Lee County.
Parnell said his company has received many more complaints about this wind farm than it has about others around the country.
"The vast majority of our complaints have to do with TV reception. This is our first experience on that front," he said.
Mark Wagner, a supporter of greater wind farm regulations in Lee County, said the letter is the "same old story." Companies put up their turbines with the approval of county governments, making many promises that they won't bother neighbors, he said.
"They say the problems won't happen, and then they do," he said. "They don't remediate the problems because you have to physically move the turbines; they won't do that. They'll pay you off and keep you quiet. That's the pattern we're seeing."
Parnell said his company is following Bureau County's ordinance on wind farms.
"We have to mitigate the issues. We're working through a process to mitigate the complaints and concerns," he said.
The Big Sky wind farm has 58 turbines in Lee County and 56 in Bureau County. It covers 13,000 acres.
Another company, Chicago-based Midwest Wind Energy, is planning the Walnut Ridge wind farm, which would be next to Big Sky's in Bureau County.
Some Walnut-area residents are trying to delay the proposed project until further study can be done. The group's members say Big Sky's issues trouble them.
The Bureau County Zoning Board of Appeals expects to decide today whether to recommend conditional-use permits for the Walnut Ridge project.
Bird Deaths Prompt Wind Rules
SOURCE: Ogdensburg Journal
Sunday April 3, 2011
By Nancy Madsen
After some wind power projects have had dramatically higher bird deaths than predicted, the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service has a set of voluntary guidelines to reduce bird deaths.
Those guidelines, if adopted by the government and developers, could force significant changes to projects, including those along the St. Lawrence River and Lake Ontario.
Bird conservation groups want the guidelines to be mandatory rules. Wind power proponents say the guidelines are too strict as they stand.
William R. Evans, director of the nonprofit Old Bird Inc., Ithaca, said the placement of wind projects is a complicated balance between the need and political momentum for renewable wind energy and the desire to protect wildlife.
“With a few projects, there’s probably not too much damage, but a major build-out would cause damage. Where do you draw the line?” he said. “We have to face the consequences.”
The guidelines call for:
* Three years of pre-construction bird population studies.
* At least two and up to five years of post-construction bird fatality studies.
* Site development decisions made as a coordinated effort among the developer, the Wildlife Service and state and tribal agencies.
* If the parties can’t agree on the adverse effects on wildlife, the service may document concerns, but the decision to proceed lies with the developer.
* Use of operational modifications – raising the speed at which turbines start turning or not operating during key migratory times or using radar to turn off turbines when flocks pass – was suggested.
* Further testing on other measures, such as multicolored turbines, and effects, such as turbine noise on birds, were suggested.
The public can comment on the guidelines until May 19.
The American Wind Energy Association, Washington, D.C., takes issue with the guidelines, saying they were changed after a committee reached a consensus on reasonable measures. The extensive studies and management based on deaths will add expense and delay construction of projects, the association said in a news release. It also adds to the number of projects that would have federal oversight, raising cost without giving additional staff to review more applications, the association said.
“While the wind industry has the responsibility to minimize the impacts of development and operations to the greatest extent practicable, and are constantly striving to achieve that goal, the reality is that every form of development, energy or otherwise, has an impact on the natural environment and the choice we are left with as a society is to pursue those avenues that have the lowest amount of impact,” AWEA siting policy director John Anderson said via email.
But the American Bird Conservancy, Washington, D.C., says the guidelines aren’t strong enough because they are optional.
“The conservancy believes we must have mandatory standards to reduce impacts from wind energy,” said Kelly Fuller, wind campaign coordinator. “The industry is not going to support standards even though they’re optional.”
A key piece of the guidelines, which was also part of the previous version, called for three years of bird population studies.
“The most important thing is that wind farms be built in areas that are not so high-risk for birds that they can’t be mitigated,” Ms. Fuller said. “The only way to find that out is by having good data to find out where those areas are.”
Mitigation measures, such as curtailing turbine use during certain seasons or times of day, also depend on the species of birds involved.
The Fish and Wildlife Service has estimated that 440,000 birds are killed each year by turbines. Because the push is to increase from 25 gigawatts now to 300 gigawatts in 2030, that number will grow, said Robert Johns, the conservancy’s public relations director.
“It doesn’t necessarily mean 12 times, but there will be a lot more birds killed,” he said. “We don’t have data on whether bigger turbines kill birds at the same rate that more smaller ones do.”
Such measures as radar to detect bird flocks and burying power lines could go a long way toward protecting bird populations, the conservancy said.
“Wind power needs to be ‘bird smart,’” Mr. Johns said. “Don’t site where lots of birds should be, employ mitigation when constructing infrastructure and compensate for lost habitat.”
The American Wind Energy Association argues that wind turbines are a very minor human cause for bird deaths. It disputes the service’s number, saying the annual number of bird deaths from turbines is about 108,000.
The association’s figure is “based on national averages as derived from over a decade of on-the-ground scientifically designed and statistically robust post-construction monitoring conducted at wind farms across the U.S. by biological consultants,” Mr. Anderson said.
The Fish and Wildlife Service extrapolated the 440,000 figure from partial data and assumptions, the association said.
Buildings kill 550 million birds per year, while power lines kill 130 million, cars kill 80 million and domestic cats kill 10 million, it said. And wind power is far less risky for bird populations than other sources of energy, it said.
Just across the Canadian border from proposed projects in Jefferson County, the Wolfe Island Wind Farm has a very high bird death rate per turbine, at 13.4 birds per turbine and a Canadian high of 0.27 birds of prey per turbine. The deaths have alarmed Canadian and U.S. conservation groups.
Mr. Evans suggested that bird deaths at St. Lawrence Wind Farm and Cape Vincent Wind Farm would be comparable to those on Wolfe Island.
“But they were proposed before the data from Wolfe Island came out,” he said. “It’s not easy to draw the line on which developments. The ones that already started could be allowed, but then others that want to come in and aren’t could say the process isn’t fair.”
Mr. Evans conducted the bird population studies for Galloo Island Wind Farm, which were “the most robust and thorough bird studies of any project in the U.S.”
The studies showed that many bird populations didn’t visit the island during migration because it is six miles offshore from the mainland.
“A substantial number of bird populations don’t want to fly over the lake,” Mr. Evans said.
Very few bird of prey species visit the island, too. A certain number of cormorants, gulls and Caspian terns fly over the island daily in search of food. But terns, the only species of concern, likely would experience 30 to 40 turbine-related deaths per year, which will hardly put a dent in a colony of 1,700 from Little Galloo Island, he said.
“It will kill terns and a substantially smaller number of raptors,” Mr. Evans said. “All these things have to be weighed against Galloo Island having one of the best wind resources on land in the Eastern U.S.”
Next story:
NO EASY ANSWERS BLOWING IN THE WIND: WIND FARMS TRICK RADAR, RAISING PUBLIC POLICY QUESTIONS
SOURCE: www.caller.com
April 2 2011
By Mark Collette,
CORPUS CHRISTI — Three or four times a day, an alarm goes off at the National Weather Service in Corpus Christi, warning of a tornado in San Patricio County.
In a dark air traffic control room at Naval Air Station Kingsville, a shadow looms on the radar screen over Kenedy County.
There is, of course, no tornado and no phantom lurking on the horizon.
But the wind farms that trigger these radar images are real, and they’re causing a collision between clean energy, military and public safety priorities.
The wind industry worries that proposed laws intended to keep turbines from interfering with military installations would thwart business in Texas, the nation’s leading wind energy state.
Weather forecasters and military officials fear turbines, which look like planes and storms on radar images, could lead to failed public warning systems and cripple the Kingsville base’s mission to train jet pilots.
For the Coastal Bend, the economic fallout of any check on the exponential growth of the industry reaches beyond the developers and the landowners who can earn around $5,000 a year on a lease for one turbine.
Shipments of wind turbine equipment through the Port of Corpus Christi in 2008 and 2009 generated $39 million in direct revenues and 256 jobs for regional businesses, according to a study by Texas A&M University-Corpus Christi economics professor Jim Lee.
As more developers pursue Coastal Bend wind projects, the potential for radar clutter rises. More than 400 turbines already have risen in San Patricio and Kenedy counties. They can produce about 1,065 megawatts, enough to power roughly 300,000 homes.
According to information compiled from government and industry sources, developers are proposing new projects in the Coastal Bend that total at least 2,445 megawatts, which could mean 800 to 1,600 more turbines.
Dottie Roark, a spokeswoman for the Electric Reliability Council of Texas, the agency that collects information on new wind projects, said many of the proposed farms never will be built for lack of financing, technical obstacles or other reasons.
But developers also may be considering projects the council doesn’t yet know about. That’s because state rules don’t require wind project developers to give any form of public notice until they request a connection to the state’s power grid. Even then, the information at ERCOT is geared toward people with a deep knowledge of electricity markets. Names of companies and locations of projects — except for the name of the county — aren’t revealed until late in the process unless a developer gives permission.
Wind developers say this arrangement promotes clean energy development and helps companies compete for leases on coveted land in a business where location means everything. Developers like the Coastal Bend because it has access to long-distance transmission lines and steady winds that are strong on hot afternoons when statewide electricity demand peaks.
Radar clutter has bred tense, delicate relationships between stakeholders who don’t want to be seen at odds with their counterparts — viewed as anti-clean energy or anti-military, for example — but who nonetheless have huge economic, environmental and safety interests to protect.
Within the National Weather Service, a careful balancing act is under way.
“There are people within the weather service who don’t want these wind farms anywhere near the radars,” said Ed Ciardi, a meteorologist at the National Weather Service Radar Operations Center in Norman, Okla., and one of the service’s leading wind farm clutter analysts.
Ciardi said despite the internal disagreements in the weather service, it has striven to work with wind developers, encouraging them to work out siting issues as early as possible.
“They don’t have to work with us,” he said. “In order not to cause them issues, we protect any data that could compromise them in a competitive way.”
That can mean not publicly disclosing potential wind farm sites unless forced by a request under the federal Freedom of Information Act, Ciardi said. Even then, the information usually is exempt from disclosure, he said.
In turn, the wind industry provides valuable information to the weather service. John Metz, warning coordination meteorologist for the weather service in Corpus Christi, said E. ON Climate and Renewables, owner of the Papalote Creek wind farm in San Patricio County, provided wind speed data after a rare January tornado cut a 20-mile swath across the Coastal Bend, ravaging trailers in the North Bay area and wrecking homes and a school in Robstown.
Some wind developers are agreeing to shut down turbines when severe weather approaches, Ciardi said.
When a weather radar
scans a wind farm, it interprets the movement of the blades as precipitation. The instruments are sensitive enough to detect bird flocks, so a wind farm — with 100 or 200 sets of blades that each stretch the length of a 747 jetliner and spin more than 100 mph at the tips in a 20 mph wind — can look like a tornado-breeding monster.
At Papalote Creek, the radar thinks it’s raining all the time. Under the right conditions, the blade movement triggers a tornado alarm, Metz said.
The radars can’t be programmed to ignore the wind farms because that could cause forecasters to miss a true storm. So far, there have been no weather warning delays or missed warnings in Corpus Christi, Metz said. The wind farms here are beyond a critical 10-mile range, allowing the radar to see easily beyond the turbines. But at least one proposed farm, near Petronila, is at the edge of the 10-mile radius.
Nationwide, wind farms haven’t caused forecasters to miss warning the public, but there have been instances of false warnings, Ciardi said.
“We’re still on the early stages of wind farm build-out,” he said. “Right now we’re only 10 percent of where the United States wants to be 10 or 20 years from now. Ten years from now, there’s likely to be more wind farms surrounding our radars, and I think that’s where we’re worried.”
It’s also a worry for Naval Air Station Kingsville, the commanding officer, Capt. Mark McLaughlin, said.
Proposed wind farms have the potential to create false radar returns throughout the airspace pilots use on their approach to the Navy base, McLaughlin said. Already, radars can lose track of planes when they fly into certain areas covered with false radar plots caused by turbines. Controllers then have to increase the distance between jets for safety.
“Increased separation means fewer training flights and decreased ability to perform our mission,” McLaughlin said.
Naval Air Station Corpus Christi officials did not respond by Friday evening.
State Sen. Juan “Chuy” Hinojosa, D-McAllen, trying to protect the base — Kingsville’s largest employer — filed a bill that would require wind developers to notify the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality and military installations of plans to build turbines within 25 miles of an installation. State Rep. J.M. Lozano, D-Kingsville, filed an identical bill in the House.
Patrick Woodson, chief development officer for E. ON, said the law would add an unnecessary layer of bureaucracy. Developers already are required to notify the Federal Aviation Administration of a wind farm project 45 days before construction, and it takes weeks to get FAA approval, he said.
Developers spend years erecting towers to test the wind and signing leases with landowners.
“There’s no secret plot here to construct wind turbines without telling anybody,” Woodson said.
Mark Hannifan, vice president of development for Tradewind Energy, said the bills provide no specific timetable for notifying the commission. Notifying too early could hurt competition, and the 25-mile requirement would take away too many potential wind farm sites, he said.
“This bill will send (wind developers) packing out of the state of Texas and send everybody packing out of the Coastal Bend.”Greg Wortham, director of the Texas Wind Energy Clearinghouse trade association, said new state regulations aren’t warranted because the FAA already has oversight and concerns over wind farm clutter are overplayed.
“The radar issue has been abused by people who just want to create an issue,” he said, “because their real story is they just don’t like wind turbines.”
Some technical solutions are on the horizon. Defense contractor Raytheon has plans to roll out new software algorithms as early as 2012 that would help military radars distinguish aircraft from wind turbines.
Patrick Paddock, an operations specialist and radar expert at Naval Air Station Kingsville, said those solutions would require years of testing and procurement processes before the military could begin to implement them. Even then, “because of the physics of this specific radar, software mitigation alone is probably not going to solve all of the problems,” he said.
4/2/11: Arrogance, a 'metaphorical Kalashnikov' and a wind lobbyist's royal 'We'-- Is it We the People or We Energies? AND Wind developers deny there is a problem while wind project residents describe their misery: Same story told with an Australian Accent AND with a Midwestern Accent AND Malfunction at the Junction: New Jersey halts approval of on-land turbines after blades fall off wind turbine
NOTE FROM THE BPWI RESEARCH NERD: Stereotyping isn't new to those of us who have expressed concerns about the wind industry's impact on people, wildlife, property values and the environment. The terms used in the following article include the usual 'NIMBY' along with 'rabid', 'shrill,' 'emotional, and divisive.'
A wind lobbyist well known for his bizarre metaphors and dismissive attitude toward people he deems 'anti-wind' adds a few more choice phrases here, this time using the pronoun "we" instead of "I"--
Describing the JCRAR's recent suspension of the Public Service Commission's wind rules, he says,
"That was a political hit job. We refer to that committee as the firing squad"
and
"We're kind of enjoying this momentary lull because we've been in a shooting war, metaphorically, with Gov. Walker since January 3. So it's nice to be able to put down the metaphorical Kalashikov and talk about strategy."
Who is 'we' in this instance? The 'business members' who pay this fellow include power giants Alliant Energy, American Transmission Company, We Energies, Madison Gas and Electric, along with big names in the wind business like Invenergy, enXco, and Horizon. Yet he's not identified as a lobbyist in this piece. Did the reporter not know?
One thing that distinguishes this article is the reporter's rare inclusion of the voices of two Fond du Lac County wind project residents who have been experiencing trouble since the turbines went on line near their homes.
Read what they have to say about their experience and decide for yourself who sounds 'shrill, rabid, emotional and divisive' in this article.
EXTRA CREDIT QUESTION: Does 'full disclosure' apply to paid lobbyists making public statements? Should lobbyists identify themselves as such to a reporter? Or should it be up to the reporter to find out by doing their homework?
AND THE WIND CRIES....UNCLE
Week of April 1, 2011
By Jim Lundstrom
Before the 1936 Rural Electrification Act brought electricity to the boonies, wind was the chief source of power for many country folk. Eventually, the windmills that once dotted the rural landscape were replaced by many forests’ worth of utility poles and probably millions of miles of cable.
It’s been lost to us how those farmers felt about their vistas being ruined and the rural nature of their property being destroyed by the ugly electrification program. Or was the prospect of entering the 20th century with the flick of a switch a salve to their bruised souls?
Wind energy never really went away, but it did go into deep hibernation for most of the rest of the 20th century, only roused from sleep by nervous consumers during the fossil fuel energy crises of the 1970s.
Ironically, the oily state of Texas is a leader in wind farms, with a generating capacity of 10,085 MW. Naturally, it boasts the world’s largest in the Roscoe Wind Farm, with 627 wind turbines covering 100,000 acres and capable of generating 781.5 megawatts, enough to power a quarter of a million homes.
Iowa has the second largest capacity with 3,675 MW, followed by California (3,177 MW), Minnesota (2,192 MW) and Washington (2,104 MW). Wisconsin produces less than 500 MW with wind power.
For all the wind in Wisconsin – it ranks 16th in the nation for quality of wind – wind supplies only 1.7% of the state’s electricity, according to the Institute for Energy Research. Coal is tops for electricity generation, providing 62.5% of the state’s power. Nuclear energy from the state’s two nuke plants accounts for 20.7% Next is natural gas with a 9.1% share, followed by hydroelectric with 2.6%, and just below wind are wood/wood-derived products and petroleum, both supplying 1.2% each of the state’s power supply.
One of the best spots in the state to generate power from wind is on the high dolomite ledge on the eastern shore of Lake Winnebago. From County A in Neenah you can see the ghostly image of the northern Fond du Lac County wind turbines, close enough to Calumet County to put the wind up folks who don’t want wind turbines in their back yard.
Fond du Lac County is home to 166 wind turbines, including the 88 in the WE Energies Blue Sky Green Field Project, which has been the largest in the state since it went online in 2008. Those are the turbines you can see across Lake Winnebago.
Fond du Lac County reaped $625,000 in revenue from the various utilities who own the wind farms for 2010. We Energies gave landowners who host the turbines in the Blue Sky Green Fields project and the townships they are in a total of $440,000.
Blue Sky Green Field is currently the largest wind farm project in the state, but owner WE Energies will surpass that next year when Glacial Hills Wind Farm goes online with 90 turbines.
The uncertainty about wind in Wisconsin and the absence of regulatory stability were cited by Invenergy on March 21 when it asked the Wisconsin Public Service Commission to terminate its application process for the proposed 150MW Ledge Wind Energy Center in southern Brown County.
With utilities required to generate 10% of their power with renewable energy by 2015, wind seems to be a good investment, just not in Wisconsin right now after the Republican-heavy Joint Committee for Review of Administrative Rules suspended the Public Service Commission’s wind siting rule on the eve it was to take effect. And not with the emotional and divisive opposition to wind from the likes of former Republican state senator Robert Welch
Welch now serves as a well-dressed hired gun for groups that oppose wind energy, including Calumet County Citizens for Responsible Energy, a group that formed when wind farms were being proposed for Brothertown and other areas in Calumet County. The group has since assisted in efforts to oppose wind development in other parts of the state.
Welch reportedly was a member of Scott Walker’s “kitchen cabinet” during his successful campaign for governor, which goes a long way in explaining why the long debated and analyzed Wisconsin Public Service Commission wind siting ruling – known as PSC 128 – was suspended by a Republican-dominated legislative committee the day before it was to go into effect on March 1.
“That was a political hit job. We refer to that committee as the firing squad,” said Michael Vickerman, executive director of Renew Wisconsin and one of the 11 members of the PSC Wind Siting Council that crafted PSC 128.
“We are actually trying to implement the state’s own policies. The state actually prefers native renewable energy over importing coal. It’s in the statutes,” Vickerman said, but adds it has been a Sisyphean task given the rabid opposition to wind in Wisconsin. “We think we’re advancing the public interest of the state. To come across this opposition can be bewildering. Four years of policy work and lobbying and negotiating, and now we’re back to 2007.”
Appearing at a March 2 public hearing on Calumet County’s proposed wind siting ordinance, which essentially mirrored PSC 128 (by law, a local ordinance could not be more restrictive than the state rules), Welch said it was the 1,250-foot setback from a non-participating landowner’s residence that killed PSC 128. He and his paying constituents have long advocated an 1,800-foot setback from a non-participating property line rather than residence.
“The proposed 1,800-foot from property line setback, that is a very strategically designed number. It systematically destroys wind power in Wisconsin,” said Jeff Carlson, who does wind siting analysis and mapping for wind projects. He said with all the other buffer zones and inherent setbacks for public roads and power lines, the 1,800-foot rule makes it virtually impossible to put all the pieces of a wind farm puzzle together.
Welch told the assembled audience that the “wholesale change in the Legislature” means that all the “hoopla” surrounding green energy mandates and global warming has “sort of gone away.”
Not gone, Vickerman said, but in a temporary holding pattern.
“We’re kind of enjoying this momentary lull because we’ve been in a shooting war, metaphorically, with Gov. Walker since Jan. 3. So it’s nice to be able to put down the metaphorical Kalashnikov and talk about strategy,” he said. “What the legislative panel did was a suspension. If the legislature wants to repeal the siting rule, it would have to do so, it has to pass both houses. We have a shot, some chance; we might succeed in stopping such a bill from clearing the legislature. If we don’t the rule does go back under a new rulemaking procedure with more hoops, the biggest one being the governor has to sign off, which wasn’t the case before.”
What’s wrong with wind farms?
Opponents of wind energy have a long list of complaints that include public subsidies for wind, aesthetics, property rights of non-participants, drop in property values, noise levels, shadow flicker, bird and bat mortality around turbines, disruption of radio and TV signals, and a host of physical complaints that a minority of wind turbine neighbors have expressed. And, of course, there are the ever-present NIMBYs who might not actually oppose wind energy, but they don’t want to look at wind turbines from their property.
The most specious argument is public subsidies of wind. Yes, there is a 10-year federal tax credit that provides 2.1 cents per kilowatt hour produced (that credit includes solar, geothermal and “closed-loop” bioenergy systems), but wind advocates point out that all forms of energy are subsidized in some way by we the people, and some in far more shameful examples of public policy than a 10-year federal tax credit. Think of all the body bags and human misery that have subsidized fossil fuel and coal. Nuclear power, anyone?
“There’s a shrill nature to the opposition to wind, whether it’s political or whatever,” said Jeff Carlson, the wind-siting analyst. “When you’re going to defend the oil supply as one of your energies, there are a whole lot of costs that are never discussed.”
More disturbing are the various problems experienced by some who live within a wind farm project.
“I can’t stand them,” said Jim Vollmer, who in November 2002 bought a home in a small valley in the Town of Marshfield in northern Fond du Lac County.
Vollmer, a mechanic by trade, also raises chickens for meat and show. Both he and his chickens have suffered medical problems he attributes to the arrival of a Blue Sky Green Field turbine 1,600 feet from his home. He says it is a combination of noise, shadow flicker and vibration that have caused him and his chickens a host of medical problems and chronic sleeplessness.
“I’ve got sound and vibration here. Headaches. Migraines. Earaches. Memory loss. Shadow. Sometimes it feels like your vision is all blurred, you can’t see straight sometimes,” he said. “My birds are the biggest thing I’m concerned with. I’ve been raising them for 22 years, showing at fairs and things. I was growing meat birds, all of a sudden the shadow started showing. With the shadow in the barn, the birds think it’s a hawk or something overhead and they’re scared to hell. They quit laying or start rampaging. They start eating eggs and then I have a hell of a time to get them to stop eating them. Low hatch rates. Ones that did hatch had all kinds of birth defects on them. I gave up on the meat birds. Tried to get compensation for the chickens, but nothing.”
In the mitigation process, WE Energies outfitted Vollmer and his neighbors with satellite TV and radio to overcome transmission problems caused by the turbines, and they installed double-thick blinds to stop the shadow flicker from entering his home. That stopped the inside flicker, but the blinds also make it dark as a tomb inside.
“It’s so dark you have to turn lights on,” he said. “I told them I had shadow in the barn, and they won’t do nothing about that. They were supposed to do shadow mitigation.”
Vollmer feels he has exhausted all his options in resolving the problems. He has been to town board meetings. He has complained to WE Energies, the PSC, the Wisconsin Department of Agriculture, Trade and Consumer Protection, various law firms, and to state Sen. Joe Liebham, one of the six Republicans on the Joint Committee for Review of Administrative Rules.
“I haven’t gotten anywhere. They all dropped the ball,” he said.
He believes his only remaining option is to sell his home and move away, but after two years on the market, “I haven’t had anyone bite on the thing yet,” he said. “I’ve had a couple people, but that was almost two years ago when I first listed it. I called another realtor up this year. I’ve had it on the market with him since Feb. 2. I dropped the price by $40,000. What really angsts me, I dropped it that much with a new realtor and that guy says we haven’t had anyone call or want to come and look at it. He said that’s not normal.”
Vollmer suggested that WE Energies buy his home.
“I told them straight up, buy the place, turn around and sell it for as much as you can get. And let me move on,” he said.
Kathy Weber runs the Pipe Meat Market in beautiful downtown Pipe. Just down County W she built a home in 2006. In 2008 a Blue Sky Green Field wind turbine was erected 850 feet from her back door.
“They built the tower too close to my house. I informed them at the time that it was too close and they put it up anyway. They are disputing the fact, saying that they had a contract before my house went up,” she said. “I told them my son has juvenile myoclonic epilepsy. I’m not saying it’s going to affect him, but I don’t want to find out. I took them at their word. The project manager for the wind farm told me after I mentioned it was too close to my house, he told me we will check the survey and get back to me. Being the country bumpkin I am, I went along with him. I came home from work one day and it was three-quarters up.”
While wind turbines as epilepsy triggers is often used as a reason against wind farms, there is little evidence to support the claim that turbines cause epileptic fits in those susceptible to them. Weber’s son, however, did have trouble concentrating, and in December moved to Fond du Lac.
Weber said she has experienced sleeping and ear problems since the turbine arrived.
“I’m 62. I never had trouble in my life with my ears,” she said.
She also learned that shadow flicker is not just a daytime problem.
“You get moon shadowing at night,” she said. “Yup, the full moon. I went to bed and I thought, ‘Oh no, don’t tell me’.”
Weber said there are times when the turbine physically makes its presence known through sound and motion.
“You can feel the difference when you’re outside and they’re moving,” she said. “People in Marytown, which is five miles away, can hear them. It’s a constant whoosh, whoosh, whoosh. In the summertime when I’m outside a lot, this may sound weird, but I start rhyming words to them, stupid words .”
Weber said WE Energies offered to lease the land from her house to the wind tower for $1,500 a year, “but I said no. I want it moved.”
But for all this, Weber is not against wind energy. She just doesn’t want a giant wind turbine literally in her back yard.
“They should not be near residential areas. They should be all together somewhere far away from residential,” she said.
“It’s not uncommon if people don’t get the resolution they expect or feel they deserve, they feel they’re not being listened to, but I can assure you we did extensive outreach efforts both prior to, during and even after in the community and with neighbors, to the extent of going door to door with participating landowners and non-participating landowners,” said Barry McNulty of WE Energies. “We’ve certainly done things to mitigate issues, too. You can’t satisfy everyone, but we’ve gone a long way to try to do so.”
“We’re not here to tell you that there are no impacts at all. There are,” said Michael Vickerman. “They tend to be localized. They don’t really have an affect on the state or the planetary environment. But when you look at the history of wind systems in this country, especially the older ones, they become accepted over time. It may take a couple of years. The howls of protest you hear now, they die off.”
Click on the image above to watch wind project residents in Australia describe life with turbines. Then click on the image below to hear what wind turbines sound like near a home in DeKalb Illinois. These are the same turbines mentioned in the following article. Read more about this wind project family's experience here: Our Life With DeKalb Wind Turbines
WIND TURBINES STILL CENTER OF DEBATE
SOURCE: Daily Chronicle, www.daily-chronicle.com
April 1, 2011
By Caitlin Mullen,
SHABBONA – Jim and Donna Nilles would like to sell their house on Leland Road.
But the Nilleses – who live within 1,800 feet of wind turbines that are part of the wind farm operated by NextEra Energy that went up in four townships in DeKalb County in late 2009 – don’t expect they’ll be able to sell their home anytime soon. Part of that is because of current economic conditions, they said, but they don’t think the wind turbines help, either.
“The main gripe we have right now is nobody listens to us,” Jim Nilles said. “Nobody comes out here.”
They are among a group of DeKalb County residents who have asked county officials – most recently at a county board meeting – to look into noise and multiple other issues related to the wind farm. One of the more recent complaints came two weeks ago when a wind turbine’s blade shattered.
But the company and the county’s planning and zoning director say NextEra has remained compliant with the terms of its permit conditions.
“We have met all of our permit conditions, and we are communicating regularly with the county as outlined in those conditions,” NextEra spokesman Steve Stengel said.
Opposing viewpoints
There has been strong opposition to the wind farm since it was first proposed.
The DeKalb County Board voted in June 2009 to grant NextEra permission to build and operate 119 wind turbines in Afton, Clinton, Milan and Shabbona townships. It’s part of a larger wind farm that included 145 total turbines in DeKalb and Lee counties. Before board approval, several hearings – including one that lasted 19 hours – were held on the proposal that brought out hundreds of people.
That opposition has continued since the farm became operational in late 2009. Mel Hass, spokesman for Citizens for Open Government – a group of local residents opposed to the wind farm and that is suing to have it shut down – said he has found many board members aren’t aware of problems with the turbines.
Residents say there are numerous issues with the turbines, including loudness, shadow flickers and interference with TV reception. Shadow flickers happen when sunlight catches the rotating blades at an angle that creates a moving shadow through windows.
Hass said many residents have called a NextEra hotline to complain about these and other issues, but he said any response from the company comes several days later, if at all.
“I don’t know what else we can do to prove our point,” Hass said. “What’s left for me and my neighbors but for us to try to resolve this on our own?”
The shattering of a turbine blade two weeks ago at Shabbona Road between Keslinger and Gurler roads is one of the recent concerns. Residents expressed concern that the shattered turbine blade and its debris could have hit a horse or a car driving near the turbine.
“Their good-neighbor policy went out the door the day the DeKalb County Board gave them those special-use permits, as far as we’re concerned,” said Beth Einsele, who claims NextEra has ignored repeated calls to respond to problems.
Stengel said the shattered blade is unusual and is under investigation. One of the wind turbines in the wind farm also experienced a broken blade in May.
“We have not experienced that anywhere else in our fleet,” Stengel said. “The cause of that is under investigation.”
Stengel said the hotline is manned during normal business hours. An answering service picks up calls that come in at other times and forwards those to the site leader, Stengel said. If someone calls to report a problem, the company is obligated to investigate it.
Stengel said the vast majority of calls have come from people who are suing the company. He said he believes those who have problems with the wind farm are in the minority. He said the facility has performed exceptionally well; there have been no injuries at the site and equipment has been well-maintained.
“I think the things that we said, I think that those things have come to be true,” Stengel said. “There is a group of individuals that are not happy with the wind farm. Those are the same individuals that are suing us in court.”
And not all residents near the wind farm have issues with the turbines. Elizabeth Armenta said she moved to her home on McGirr Road last year and isn’t bothered by the wind turbines. She doesn’t live close enough to experience shadow flickers, and she said she can’t hear the turbines unless it’s very quiet.
Kit Tjelle, who lives on Lee Road, said she and her husband Kevin feared the worst before the turbines were installed, but she said they’ve been pleasantly surprised to find they appreciate their beauty and clean design. A few turbines stand just beyond their backyard.
“They don’t bug us at all. At all,” Tjelle said. “They’ve kind of become part of our landscape.”
Paul Miller, the county’s director of planning and zoning, said the county monitors and follows up on the 36 conditions that were part of the county’s approval of the wind farm, including things like setbacks from structures and property lines, and a property value guarantee.
“To date, we have not found them in violation of any of those conditions,” Miller said.
Lawsuit still pending
Citizens for Open Government filed a lawsuit in July 2009 that was dismissed later that year because it lacked factual evidence. The group filed an amended complaint in January 2010, asking that the wind farm be shut down and the turbines dismantled. In June 2010, a judge rejected NextEra’s motion to dismiss the lawsuit.
The lawsuit names NextEra Energy, the county board and the nearly 100 landowners who allowed turbines to be installed on their property. The lawsuit alleges that the county board overstepped its zoning authority when it authorized the special-use zoning permits for agricultural land. County officials have said the project is allowed under a special-use clause that permits “essential service structures.”
John Farrell, who manages the civil division of the DeKalb County State’s Attorney’s Office, said the case has been pending for a while, but it’s too early to say where it’s going.
Next story
STATE SHUTES DOWN ON SHORE WIND TURBINE PROGRAM AFTER MAJOR MALFUNCTION
March 25, 2011
by Tom Johnson
The state has shut down its on-land wind turbine program for the time being after an incident earlier this month when three blades suddenly came off a turbine at a farm and residence in Forked River.
The incident, which is under investigation, led the state Office of Clean Energy, to halt temporarily accepting applications for its Renewable Energy Incentive Program (REIP) wind project until authorities can determine how the blades became disengaged, according to Greg Reinert, a spokesman for the Board of Public Utilities (BPU).
The problem occurred on March 2 when a still unexplained major malfunction on a recently installed wind turbine caused all three blades to break loose, Reinert said.
On March 8, the clean energy office staff directed the program coordinator to issue a notice to stakeholders advising that "Effective immediately, there is a temporary hold on all new REIP wind applications and wind rebate processing until further notice."
Ellen Carey, a spokeswoman with the American Wind Energy Association, said she had never heard of this type of accident. "I would say it is an abnormal occurrence," she said
Land and Sea
The state’s efforts to develop wind energy on land have been dwarfed by its goals to build a vibrant offshore wind industry, an ambition that aims to develop 3,000 megawatts of wind farms off the coast of New Jersey.
Four developers have announced plans to build offshore wind farms from 3 miles to about 16 miles out in the ocean.
In comparison, the onshore wind efforts are much less ambitious, in part, because the wind resources pale in comparison to what is available offshore. Still, the Office of Clean Energy had overseen the installation of 38 wind systems, eligible for up to $5 million in rebates and grants, according to Reinert. The total installed capacity is 8.0291 megawatts.
In addition, there are another 37 wind projects approved as of March 18, with a total capacity of 4.64 megawatts and eligible for up to $3.5 million in state incentives..
It is uncertain when the office will begin accepting applications again. Like last year, the clean energy office has seen its funds diverted to help balance the state budget. Under Gov. Chris Christie’s proposed budget for the next fiscal year, $52.5 million from the Clean Energy Fund will be set aside.
4/1/11 How Green is a Bat Killing Turbine? Dead bats mean more corn borer larvae, more pesticides and lower crop yields AND When wind developers say MAKE ME: Invenergy ignores PSC's requests for latest bird and bat post construction mortality study AND It's April Fool's day but this is no foolin'--- Where wind developers have been prospecting in Wisconsin
NOTE FROM THE BPWI RESEARCH NERD: According to numbers in a previous bird and bat post construction mortality study paid for by Invenergy for the Forward Wind project located near the Horicon Marsh, the turbine related bat-kill numbers are staggering: it appears that well over 10,000 bats have been killed in just three years of the Forward project's operation.
The turbine related bat kill rate in Wisconsin is ten times higher than the national average and the second highest in North America. Yet nothing is being done about it. In fact, the Public Service Commission can't even get Invenergy to submit a long-past-due required mortality report.
Who ya' gonna call?
Better Plan has contacted the Sierra Club, the Nature Conservancy, the Audubon Society, Bat Conservation International and a multitude of journalists with this information but so far no one has moved to look more closely into this story.
Meanwhile, bats are being slaughtered by the thousands in Wisconsin wind projects. Horton may hear a Who but at the moment environmentalists and media aren't taking any calls from Horton.
Next Story
DEAR EMPEROR OF INVENERGY, STOP ME IF YOU'VE HEARD THIS ONE: THE PSC WANTS TO KNOW WHY YOU WON'T RELEASE YOUR LATEST POST CONSTRUCTION BIRD AND BAT MORTALITY STUDY
"Agency staff has repeatedly requested the required reports. To date, no satisfactory explanation has been received for their delay nor a firm date established for their submission. At minimum, submittal of the final report is required to comply with the requirements of the Commission’s Final Decision for this docket. Please submit the required reports."
-PSC's letter to Invenergy dated 3/25/2011
FROM: DAN SAGE at the PUBLIC SERVICE COMMISSION OF WISCONSIN
TO: MIKE COLLINS, INVENERGY LLC, CHICAGO, ILLINOIS
DATE: MARCH 25th, 2011
Dear Mr. Collins:
In the Commission’s Final Decision on July 14, 2005, Forward Energy LLC (Forward) was required to conduct post-construction bird and bat studies in consultation with the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service (USFWS) and the Wisconsin Department of Natural Resources (DNR).
Data collected from these studies were to be submitted to agency staff on a quarterly basis. In addition, Forward was required to conduct a population viability analysis with associated sensitivity analyses for bat populations.
As a means of complying with the Commission’s Final Decision, three study plans were reviewed and approved by agency staff. These studies included a bird use, a bat use, and a bird/bat mortality study. Within each of these plans was an agreed-to timetable for field study and report submittal.
Forward initiated field studies in July 2008. The bat use and bird use studies ended in November 2009. Data collection for the mortality study ended in May 2010. The last report received from Forward summarized data collected through February 1, 2010. Forward has not submitted a report summarizing the data collected during the period of April through May of 2010.
Additionally, the final report has not been submitted. The final report is required to contain at a minimum the following items:
Summary of all field data collected during the years of 2008, 2009, and 2010;
Comparison of pre-construction and post-construction relative abundance and diversity of birds;
Impact gradient analysis of bird use and behavioral data relative to the Horicon National Wildlife Refuge;
Analysis of the changes in pre-construction versus post-construction avian habitat;
Analysis of the type and number of bats that use the Forward airspace compared to the bat fatality estimates resulting from the wind turbines;
Mortality estimates incorporating scavenger and searcher efficiency rates using the best available estimation formulas and reported as avian and bat fatalities per megawatt per year and per turbine per year;
Additional analyses including comparing the mortality at control sites to the mortality at turbine sites and correlation analyses between mortality and weather, turbine locations, turbine operating status, and bird and bat activity.
Agency staff has repeatedly requested the required reports.
To date, no satisfactory explanation has been received for their delay nor a firm date established for their submission. At minimum, submittal of the final report is required to comply with the requirements of the Commission’s Final Decision for this docket. Please submit the required reports.
If you have questions regarding this matter, please contact Marilyn M. Weiss by telephone at (608) 241-0084 or by e-mail at marilyn.weiss@wisconsin.gov.
Sincerely,
/s/ Dan Sage
Dan Sage
Assistant Administrator
Gas and Energy Division
NOTE: Click on the image below to watch a video about Invenergy's Forward Project wind turbines alongside Wisconsin's famed Horicon Marsh and near the Neda Mines, home to the largest bat population in the state.
NEXT STORY
BATS WORTH BILLIONS TO AGRICULTURE:
PEST-CONTROL SERVICES AT RISK
April 1, 2011
BOSTON, -- Thomas Kunz, Warren Distinguished Professor in Boston University's Department of Biology, has coauthored an analysis published this week in the journal Science that shows how declines of bat populations caused by a new wildlife disease and fatalities at industrial-scale wind turbines could lead to substantial economic losses on the farm.
Natural pest-control services provided by insect-eating bats in the United States likely save the U.S. agricultural industry at least $3 billion a year, and yet insectivorous bats are among the most overlooked economically important, non-domesticated animals in North America, noted the study's authors, scientists from the University of Pretoria (South Africa), the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS), the University of Tennessee, and Boston University.
"People often ask why we should care about bats," said Paul Cryan, a USGS research scientist at the Fort Collins Science Center and one of the study's authors. "This analysis suggests that bats are saving us big bucks by gobbling up insects that eat or damage our crops. It is obviously beneficial that insectivorous bats are patrolling the skies at night above our fields and forests—these bats deserve help."
The value of the pest-control services to agriculture provided by bats in the U.S. alone range from a low of $3.7 billion to a high of $53 billion a year, the authors estimated. They also warned that noticeable economic losses to North American agriculture could well occur in the next 4 to 5 years because of the double-whammy effect of bat losses due to the emerging disease white-nose syndrome and fatalities of certain migratory bats at wind-energy facilities. In the Northeast, however, where white-nose syndrome has killed more than one million bats in the past few years, the effects could be evident sooner.
"Bats eat tremendous quantities of flying pest insects, so the loss of bats is likely to have long-term effects on agricultural and ecological systems," said Justin Boyles, a researcher with the University of Pretoria and the lead author of the study. "Consequently, not only is the conservation of bats important for the well-being of ecosystems, but it is also in the best interest of national and international economies."
A single little brown bat, which has a body no bigger than an adult human thumb, can eat 4 to 8 grams (the weight of about a grape or two) of insects each night, the authors note. Although this may not sound like much, it adds up—the loss of one million bats in the Northeast has probably resulted in between 660 and 1,320 metric tons of insects no longer being eaten each year by bats in the region.
"Additionally, because the agricultural value of bats in the Northeast is small compared with other parts of the country, such losses could be even more substantial in the extensive agricultural regions in the Midwest and the Great Plains, where wind-energy development is booming and the fungus responsible for white-nose syndrome was recently detected," said Kunz.
Although these estimates include the costs of pesticide applications that are not needed because of the pest-control services bats provide, Boyles and his colleagues said they did not account for the detrimental effects of pesticides on ecosystems or the economic benefits of bats suppressing pest insects in forests, both of which may be considerable.
The loss of bats to white-nose syndrome has largely occurred during the past 4 years, after the disease first appeared in upstate New York. Since then, the fungus thought to cause white-nose syndrome has spread southward and westward and has now been found in 15 states and in eastern Canada. Bat declines in the Northeast, the most severely affected region in the U.S. thus far, have exceeded 70 percent. Populations of at least one species, the little brown bat, have declined so precipitously that scientists expect the species to disappear from the region within the next 20 years.
The losses of bats at wind-power facilities, however, pose a different kind of problem, according to the authors. Although several species of migratory tree-dwelling bats are particularly susceptible to wind turbines, continental-scale monitoring programs are not in place and reasons for the particular susceptibility of some bat species to turbines remain a mystery, Cryan said.
By one estimate, published by Kunz and colleagues in 2007, about 33,000 to 111,000 bats will die each year by 2020 just in the mountainous region of the Mid-Atlantic Highlands from direct collisions with wind turbines as well from lung damage caused by pressure changes bats experience when flying near moving turbine blades. In addition, surprisingly large numbers of bats are dying at wind-energy facilities in other regions of North America.
"We hope that our analysis gets people thinking more about the value of bats and why their conservation is important," said Gary McCracken, a University of Tennessee professor and co-author of the analysis. "The bottom line is that the natural pest-control services provided by bats save farmers a lot of money."
The authors conclude that solutions to reduce the impacts of white-nose syndrome and fatalities from wind turbines may be possible in the coming years, but that such work is most likely to be driven by public support that will require a wider awareness of the benefits of insectivorous bats.
The article, "Economic importance of bats in agriculture," appears in the April 1 edition of Science. Authors are J.G. Boyles, P. Cryan, G. McCracken and T. Kunz.
NEXT STORY: WHERE ARE THE WIND DEVELOPERS PROSPECTING IN WISCONSIN?
Wisconsin wind project locations: proposed, existing and being built:
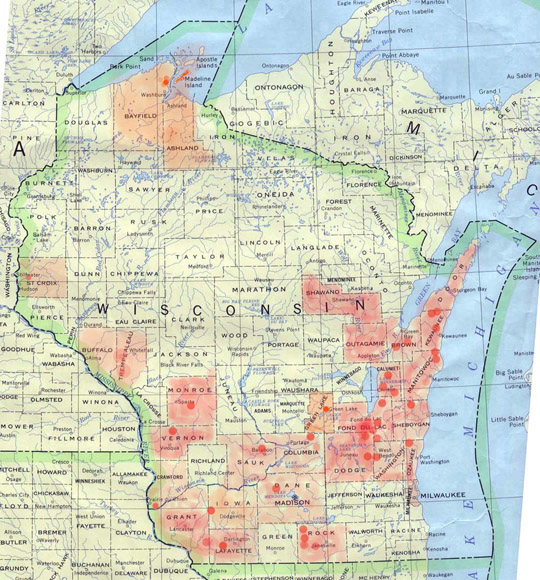
WIND DEVELOPERS HAVE BEEN SPOTTED IN:
ADAMS COUNTY
Town of Lincoln
ASHLAND COUNTY
Madeline Island
BAYFIELD COUNTY
Town of Bayfield
BROWN COUNTY
Towns Glenmore, Greenleaf, Holland, Morrison, Wrightstown
Invenergy's Ledge Wind project (currently on hold)
Emerging Energy's Shirley Wind project (Town of Glenmore. Now under construction)
BUFFALO COUNTY
CALUMET COUNTY
Towns of Brothertown, Charlesburg, Chilton, New Holstein, Rantoul, Stockbridge
COLUMBIA COUNTY
We Energies Glacier Hills project (under construction)
Towns of Arlington, Cambria, Leeds, Randolph and Scott.
CLICK HERE TO DOWNLOAD GLACIER HILLS TURBINE LOCATION MAP
CRAWFORD COUNTY
Invenergy is prospecting south of Prairie Du Chien
DANE COUNTY
Town of Springfield
EcoEnergy developed the project, then sold it to WAVE WIND LLC
According to news stories, Wave Wind was looking for a contract with WPPI to buy the power. The outcome of negotiations between these two parties is unknown as of September 2010
News stories:
Dane County's wind farm fate rests with WPPI
DODGE COUNTY
Towns of Herman and Rubicon
DOOR COUNTY
Town of Clay Banks
Download Clay Banks Wind ordinance
FOND DU LAC COUNTY
Towns of Ashford, Brownsville, Byron, Eden, Empire
GRANT COUNTY
Cuba City, Towns of Hazel Green, Paris, Plattville, Smelser, Patch Grove, Mt. Hope
GREEN LAKE COUNTY
Town of Green Lake
IOWA COUNTY
Town of Montfort
KEWAUNEE COUNTY
Town of Casco
LAFAYETTE COUNTY
Towns of Belmont and Seymour
MANITOWOC COUNTY
Towns of Mishicot, Two Creeks, Two Rivers
Town of Centerville Developer: Spanish company www.urielwind.com
For the latest information on Manitowoc County projects visit Windcows.com
MONROE COUNTY
Towns of Ridgeville and Wilton
OUTGAMIE COUNTY
Town of Kaukauna
OZAUKEE COUNTY
Town of Freedonia
ROCK COUNTY
Towns of Center, Janesville, Spring Valley, Magnolia, Union
Landowner contracts in the Towns of Magnolia and Union originally secured by EcoEnergy have been sold to Spanish wind giant Acciona . Acciona says it has suspended the project because of low wind resource. However, they still own the project and can sell it.
SHEBOYGAN COUNTY
Town of Rhine
ST CROIX COUNTY
Town of Forest
TREMPEALEAU COUNTY
Town of Arcadia
Town of Ettrick
Download Trempealeau County wind ordinance
VERNON COUNTY
Town of Westby
WASHINGTON COUNTY
Towns of Addison, Nabob, and West Bend
3/31/11 Local elections tied to wind development in Brown County AND Big wind lawsuit in little St. Croix county AND Wind Whirl over cancelled projects: How much of it is spin? AND Wind blade factory falls through: carrot on end of stick could have been a mirage AND Hello Windmill, Bye Bye Birdie
WIND FARMS REMAIN AN ISSUE IN GLENMORE, MORRISON
Source: Green Bay Press Gazette
March 31, 2011
By Doug Schneider
Wind farms remain a campaign issue in two southern Brown County towns, despite a company's recent decision to cancel plans for 100 wind turbines in Morrison, Glenmore and other nearby communities.
Invenergy LLC said it would not pursue permits for a wind farm in the area, but campaign signs related to wind energy continue to dot the landscape, and candidates say they still need to be prepared with future proposals that could affect residents' quality of life.
"We have to keep in mind that there are other projects like this out there, smaller developments," said Todd Christensen, who is seeking re-election as Morrison town board chairman, "and there could be more in the future."
Invenergy would have put 54 turbines in Morrison, four in Glenmore, and others in Wrightstown and Holland. Because some town officials expect there will be other developments proposed, towns are banding together to push for consistent regulations on issues related to windmills, and are asking state officials to consider their concerns. A handful of wind turbines were built as part of another project off Wisconsin 96 near the hamlet of Shirley.
But candidates also say there are issues beyond wind-energy regulation.
Cliff Hammond, who is challenging Christensen, said the next town board also will need to work to maintain a balanced budget as financial support from the state and county decline.
Kriss Schmidt, who is running for board chairperson in Glenmore, said board members will have to make sure basic services like snowplowing and road-patching are maintained.
Pat Kolarik, who also is running for Glenmore board chair, said the key for elected officials will be to focus on maintaining residents' quality of life whether the issue is wind energy or something else.
"There are going to be a number of challenges we have to address — budget, services, appropriate setbacks for any structure," she said. "The goal for me would be to work with residents on appropriate solutions."
ENERGY SOLUTION OR LEGAL TROUBLE?
March 31 2011
"The controversial energy project in Forest has come under fire and may be stopped by a federal lawsuit which was filed by a citizens’ group in February."
A legal battle in northeastern St. Croix County highlights the difficult issues of wind-generated power. Talk to anyone and they will, in general terms, talk about wind power as a good, efficient and cheap energy source for the times — be it today or tomorrow.
Try finding a location to construct wind generators and suddenly you’ve got yourself a first-class controversy, complete with arguments among neighbors, recalls and lawsuits.
Such is the case in St. Croix County in the town of Forest.
The controversial energy project in Forest has come under fire and may be stopped by a federal lawsuit which was filed by a citizens’ group in February. That suit was also supported by action of a new town board that was elected through a successful recall election. The former board had approved the proposed wind energy project last summer.
A citizens’ lawsuit was filed in February. In March, the new town of Forest board voted to rescind a wind energy development agreement and other approvals that had been granted to a wind developer. The project, being proposed by a private developer named Emerging Energies, is in jeopardy.
The project in Forest called for 39 wind towers. Each tower stands about 500 feet tall.
Many landowners in the town had signed leases with the wind firm, but were prohibited from discussing the project. When the rest of the town’s residents got “wind” of the deals, the uprising began.
Now there are battles over setbacks, noise, quality of life, health, property value, safety and more. Emerging Energies, LLC, has also threat-ened the new town board with legal action.
A similar scenario developed in the eastern part of the state when a Chicago wind energy developer, Invenergy LLC, dropped its plan to build a large wind farm near Green Bay.
Opponents in the Green Bay area are expressing the same concerns and claim they will continue to work to prevent the “irresponsible development of industrial wind projects.”
State energy regulators are now trying to come up with a plan to help support wind projects. Regulators may be asked to go back to the drawing board to develop statewide rules governing wind power projects, under a bill to be considered this week.
The Legislature’s joint committee for review of administrative rules voted earlier this month to temporarily block a wind farm site rule developed by the state Public Service Commission.
Supporters of wind energy development say legal problems will stall development, leading to a loss of jobs tied to wind turbine construction as well as revenue for host property owners and local governments. There seems to be plenty of controversy over, among other things, setbacks for wind towers.
A property rights bill introduced by Gov. Scott Walker in January would restrict wind towers from being placed less than 1,800 feet from a property line. That bill had the apparent support of wind farm opponents and the Wisconsin Realtors Association.
In its most recent wind farm decision, the PSC ruled that 1,250-foot setbacks be required for We Energies’ Glacier Hills Wind Park, now under construction in Columbia County.
The bottom line is, when wind towers begin popping up in either populated areas, or rural countryside, there is likely to be plenty of opposition. A group of wind towers doesn’t do much for the scenic value of any topography.
Despite all the virtues of wind power, developing a power source to a degree where it would have a significant impact could be difficult when facing “not in my backyard” neighborhoods.
MIDWEST WIND SUSPENDS DEVELOPMENT WORK IN STATE
"Wind industry representatives said the PSC rule was restrictive because it set specific decibel limits for turbine noise and shadow flicker restrictions as well as setbacks."
March 31, 2011
By Thomas Content
Midwest Wind Energy is suspending development of two wind farms in Wisconsin, the Illinois company said Wednesday.
The company developed the Butler Ridge wind farm in Dodge County and the Cedar Ridge project in Fond du Lac County, projects now owned and operated by other companies.
Midwest Wind said it was actively working on a 98-megawatt wind farm in Calumet County and another project for which a location had not yet been announced.
Midwest Wind cited development opportunities in other states at a time when Wisconsin policymakers are moving to restrict wind farm development.
"Most states are clearly open for renewable energy development and the economic development dollars and jobs that come with it,” said Stefan Noe, company president. “So long as there are states rolling out the welcome mat it doesn't make sense to devote significant dollars to a state that is creating unreasonable roadblocks for wind development."
The action came one week after Invenergy of Chicago canceled plans to develop a large wind farm near Green Bay, and one day after a legislative committee voted to introduce a bill sending wind siting rules back to the state Public Service Commission for more work.
Republican lawmakers and Gov. Scott Walker have said the PSC rule allowed turbines to be built too close to nearby homes. Wind industry representatives said the PSC rule was restrictive because it set specific decibel limits for turbine noise and shadow flicker restrictions as well as setbacks.
A bill that passed in the Legislature two years ago called on the PSC to set up a uniform standard for wind projects across the state, to replace a patchwork of local rules and moratoriums that were in place with regard to wind projects.
Keith Reopelle, senior policy director at the environmental group Clean Wisconsin, said the new chair of the PSC, Phil Montgomery, was a co-sponsor and supporter of the bill that called on the PSC to set statewide standards. He said he hoped the agency would move quickly to develop a workable set of rules.
When the bill was introduced in 2009, Montgomery – then a state lawmaker from Brown County and ranking Republican on the Assembly energy and utilities committee - released a statement in support of a uniform state standard.
“Wind power is job-creating power,” Montgomery said in April 2009. “A fair and uniform state standard for siting wind developments will create an environment of investment in our state while moving us closer to our green energy goals.”
WIND TURBINE PLANT ON HOLD
Source: Wisconsin Rapids Daily Tribune
March 31, 2011
By Nathaniel Shuda
"I think we had to give them every opportunity to succeed," council member Lee Albrecht said. "You have this carrot dangling out there that there are 600 jobs on the horizon; I think you have to do whatever you can to have that carrot come to you."
Wisconsin Rapids is ready to buy back land it sold to a local company that two years ago announced plans to build a wind-turbine blade manufacturing plant on the property.
Energy Composites Corp. faces a Friday deadline to either reach an agreement with Wisconsin Rapids or sell the nearly 94 acres of land back to the city at the original purchasing price, Mayor Mary Jo Carson said.
Carson said the sale doesn't necessarily mean the project is dead, but it won't happen right now.
"Obviously, ECC doesn't want to hold us up in reference to that land, which we thank them for," she said. "We appreciate their interest in their hometown."
Carson said City Attorney Sue Schill has been working with the company's attorney to reach a buy-back agreement.
On March 31, 2009, the company announced plans to build a 350,000-square-foot plant in the Rapids East Commerce Center that would create at least 400 local jobs. Since then, those plans expanded to 535,000 square feet and more than 600 positions.
To facilitate the project, the city later sold the Wisconsin Rapids-based company 93.7 acres of land in the Rapids East Commerce Center for $500 an acre -- a 90 percent discount from the typical asking price -- plus a $1,000 option fee, for a total price of $47,850.
Under the pending agreement, the city would buy back the land at the same price for which it sold it, Carson said.
"I'm glad to see it being sold back to the city at the original price," City Council member Marion Hokamp said. "The sooner they do it, the better it's going to be. Maybe we're going to get somebody else interested (in the property)."
As part of the original development agreement, the city would have paid $1.5 million for infrastructure costs, including extending city streets and expanding railroad access to the property, and $6,000 for each full-time job the company created on or before Dec. 31, 2012, up to $3.8 million.
At this point, Wisconsin Rapids has not invested any money in the project, city Finance Director Tim Desorcy said.
A decline in bond market conditions led company officials to put the project on hold while they searched for investors. Those efforts have been unsuccessful.
Hokamp, who has publicly criticized Energy Composites for a lack of action, said the city should have bought the property back sooner. She remained skeptical of the project throughout the process.
"Way back when they started, I never thought it was going to be done," she said. "They knew they weren't going to have anything out there a long time ago."
Other council members do not regret giving the company so long to bring the plan to fruition.
"I think we had to give them every opportunity to succeed," council member Lee Albrecht said. "You have this carrot dangling out there that there are 600 jobs on the horizon; I think you have to do whatever you can to have that carrot come to you."
WIND FARMS THREATEN MANY BIRD SPECIES WITH EXTINCTION
SOURCE Save The Eagles Foundation
STEI's president, Mark Duchamp, objects to the wind industry comparing bird mortality at windfarms to that from other causes related to human activities. These other threats have already reduced bird populations worldwide, he said, and are continuing to do so.
"But mortality caused by windfarms and their power lines is new and additional", he adds, "and like the proverbial last drop that spills the glass, its effects will be upsetting.
To wit the Tasmanian Wedge-tailed Eagle, which has been condemned to extinction by the construction of 7 windfarms in its habitat" (1).
Another important difference, says Duchamp, is that the other threats can't be easily stopped, whereas poorly-sited windfarm projects can. The Spanish Ornithological Society (SEO/Birdlife) recommended this month that windfarms no longer be built in natural areas, but in urban and industrial areas instead (2).
One week later, SEO/Birdlife revealed that bird mortality caused by windfarms and power lines was much higher than previously thought. For the Spanish region of Castilla La Mancha, they estimate it to be "1.3 million birds a year, many of them in danger of extinction like the Imperial Eagle, the Bonelli´s Eagle or the Lesser Kestrel". And they added: "(this is) a considerable number which proves that windfarms have a great capacity for killing birds". (3)
"This is what I have been claiming for 9 years", says Duchamp, "but only this month did SEO recognize the danger. During all that time I have been treated as a heretic, and was banned from ornithology forums where my whistle-blowing was causing discomfort in the profession."
The French naturalist, who lives in Spain, has been vindicated at last. He praises the American Bird Conservancy, Birdlife Bulgaria, and SEO for their firm stand against improperly sited windfarms, but laments that it will take more years before the most prominent bird societies do likewise. Conflicts of interests are at the root of the problem, he says.
STEI warns that, if we are to save our emblematic bird species from this new threat, it is urgent to impose a moratorium on windfarm construction and to call for a really independent commission to investigate the whole windfarm matter, starting with the effectiveness of this intermittent, unreliable, and ruinous form of energy.
Duchamp founded Save the Eagles International in 2009, to raise awareness and to publish inconvenient bird mortality statistics that most bird societies fail to make available to the public. He has launched today the STEI website where these numbers and their sources can be found:
REFERENCES
(1) - Wind farms: suspicious error by consultant condemns Tasmanian eagle to extinction.
(2) - SEO Birdlife: " Castilla-La Mancha "debe abandonar el viejo modelo de grandes centrales de generación eléctrica situadas en plena naturaleza y alejadas de los puntos de consumo y fomentar la generación eléctrica en suelo urbano e industrial".
Translation: "Castilla-La Mancha "must abandon the old model of large power plants located in natural habitats, far away from where the energy is consumed, and promote electrical generation in urban and industrial zones."
(3) - SEO Birdlife: "1,3 millones de aves al año... un número considerable con el que se demuestra que los parques eólicos tienen «una gran capacidad para matar aves»."
Translation: "1.3 millon birds a year... a considerable number which proves that windfarms have a great capacity for killing birds "