11/29/11 Wind turbines on summer vacation during Texas heatwave AND New uses for disturbing low frequency noise AND Down under, 2 kilometer setback endangers wind developer wallets AND siting rules in US protect wind developer's wallets by endangering Golden Eagles AND It's a small small small small world when it comes to troubles with wind turbines
From the U.S.
TEXAS WIND ENERGY FAILS AGAIN
Source: National Review Online, www.nationalreview.com
August 29, 2011
Robert Bryce
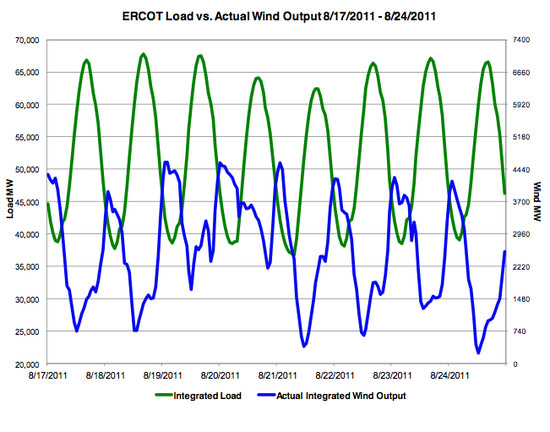
Wednesday brought yet another unspeakably hot day to Texas and, alas, it was yet another day when wind energy failed the state’s consumers.
Indeed, as record heat and drought continue to hammer the Lone Star State, the inanity of the state’s multi-billion-dollar spending spree on wind energy becomes ever more apparent. On Wednesday afternoon, ERCOT, the state’s grid operator, declared a power emergency as some of the state’s generation units began to falter under the soaring demand for electricity. Electricity demand hit 66,552 megawatts, about 1,700 megawatts shy of the record set on August 3.
As I wrote in these pages earlier this month, Texas has 10,135 megawatts of installed wind-generation capacity, which is nearly three times as much as any other state. And yet, on Wednesday, all of the state’s wind turbines mustered just 880 megawatts of power when electricity was needed the most. Put another way, even though wind turbines account for about 10 percent of Texas’s 103,000 megawatts of summer electricity-generation capacity, wind energy was able to provide just 1.3 percent of the juice the state needed on Wednesday afternoon to keep the lights on and the air conditioners humming.
None of this should be surprising. For years, ERCOT has counted just 8.7 percent of the state’s installed wind-generation capacity as “dependable capacity at peak.” What happened on Wednesday? Just 880 megawatts out of 10,135 megawatts of wind capacity — 8.68 percent — was actually moving electrons when consumers needed those electrons the most.
Apologists for the wind industry point to a single day in February, when, during a record cold snap, the state’s wind turbines were able to produce electricity when the grid was being stressed. Fine. On one day, wind generators produced more than expected. But the wind industry’s lobbyists want consumers to ignore this sun-bleached truth: Texas has far more super-hot days than it does frigid ones. Indeed, here in Austin, where I live, we’ve already had 70 days this summer with temperatures over 100 degrees, and there’s still no relief in sight. And on nearly every one of those hot days, ERCOT’s wind capacity has been AWOL. Each afternoon, as the temperature — and electricity demand — soars, the wind dies down:
This summer’s high demand for electricity has caught ERCOT off guard. In June, the grid operator projected that Texas’s electricity demand would not set any new records this summer. But demand is already exceeding levels that ERCOT didn’t expect to see until 2014. Over the past few weeks, as demand has strained the Texas grid, electricity prices have risen as high as $3,000 per megawatt-hour on the wholesale market, and large industrial users have been forced to curtail consumption in order to avoid blackouts.
And yet — and yet — the state is spending billions on projects that focus on wind energy rather than on conventional generation capacity. As Kate Galbraith of the Texas Tribune reported recently, the Texas Public Utility Commission is preparing the state’s ratepayers for higher prices. Consumers will soon be paying for new transmission lines that are being built solely so that the subsidy-dependent wind-energy profiteers can move electricity from their distant wind projects to consumers in urban areas.
Galbraith reports that “the cost of building thousands of miles of transmission lines to carry wind power across Texas is now estimated at $6.79 billion, a 38 percent increase from the initial projection three years ago.” What will that mean for the state’s ratepayers? Higher electricity bills. Before the end of the year, the companies building the transmission lines are expected to begin applying for “rate recovery.” The result, writes Galbraith, will be charges that “could amount to $4 to $5 per month on Texas electric bills, for years.”
Imagine what the state’s grid might look like if Texas, which produces about 30 percent of America’s gas, had spent its money on natural-gas-fired electricity instead of wind. The latest data from the Energy Information Administration shows that wind-generated electricity costs about 50 percent more than that produced by natural-gas-fired generators. Thus, not only would Texas consumers be saving money on their electric bills, the state government would be earning more royalties from gas produced and consumed in the state.
Further, consider what might be happening had the state kept the $6.79 billion it’s now spending on wind-energy transmission lines and instead allocated it to new natural-gas-fired generators. The latest data from the Energy Information Administration show that building a megawatt of new wind capacity costs $2.43 million — that’s up by 21 percent over the year-earlier costs — while a new megawatt of gas-fired capacity costs a bit less than $1 million, a drop of 3 percent from year-earlier estimates.
Under that scenario, Texas could have built 6,900 megawatts of new gas-fired capacity for what the state is now spending on wind-related transmission lines alone. Even if we assume the new gas-fired units were operating at just 50 percent of their design capacity, those generators would still be capable of providing far more reliable juice to the grid than what is being derived from the state’s wind turbines during times of peak demand.
Unfortunately, none of those scenarios have played out. Instead, Texas ratepayers are being forced to pay billions for wind-generation and transmission capacity that is proving to be ultra-expensive and redundant at a time when the state’s thirst for electricity is breaking records.
A final point: Keep in mind that the Lone Star wind boondoggle is not the result of Democratic rule. Environmentalists have never gained much purchase at the Texas capitol. In fact, the state hasn’t had a Democrat in statewide office since Bob Bullock retired as lieutenant governor, and Garry Mauro retired from the General Land Office, back in 1999. That same year, Gov. George W. Bush signed legislation that created a renewable-energy mandate in the state.
What about Rick Perry, a politico who frequently invokes his support for the free market? In 2005, he signed a mandate requiring the state to have at least 6,000 megawatts of renewable capacity by 2015. Perry’s support has been so strong that a wind-energy lobbyist recently told the New York Times that the governor, who’s now a leading contender for the White House, has “been a stalwart in defense of wind energy in this state, no question about it.”
And during his last election campaign, Sen. John Cornyn, one of the Senate’s most conservative members, ran TV ads showing pretty pictures of — what else? — wind turbines.
NEXT STORY:
THE NEW POLICE SIREN: YOU'LL FEEL IT COMING
SOURCE: The New York Times
February 25, 2011
By Ariel Kaminer
Joe Bader tried setting the two tones of his invention four notes apart on the musical scale, but the result sounded like music, not a siren. Same thing when he played around with a five-note interval. But when he set the two tones apart by two octaves and gave the siren a test run outside the Florida Highway Patrol headquarters in Tallahassee, the effect was so attention-grabbing that people came streaming out of the building to see what the strange sound, with its unfamiliar vibrations, could possibly be.
Which was precisely what Mr. Bader, a vice president at the security firm Federal Signal Corporation, was going for: a siren that would make people sit up and take notice — even people accustomed to hearing sirens all the time. Even people wearing ear buds or talking on the phone. Even people insulated from street noise by a layer of glass and steel. Even New Yorkers.
Rumblers, as Mr. Bader called his invention, achieve their striking effect with a low-frequency tone, in the range of 180 to 360 hertz (between the 33rd and the 46th key on a standard piano keyboard), which penetrates hard surfaces like car doors and windows better than a high tone does. When it is paired with the wail of a standard siren, the effect is hard to ignore — like the combination of a bagpipe’s high chanter and low drone, or perhaps like a train whistle and the caboose that moves that whistle through space.
Following the lead of some other municipalities, the New York Police Department gave the devices two limited test runs beginning in 2007. It liked what it heard, with the result that a Rumbler will be coming soon to a police car near you — perhaps one speeding right at you in a high-speed chase through traffic- and pedestrian-clogged streets. And eventually to about 5,000 of the department’s more than 8,000 vehicles.
Some New Yorkers have already raised concerns that the Rumbler’s low-frequency vibration could be injurious to their health. The Police Department insists that there is nothing to worry about and invited me to experience the effect for myself. But when Officer Joe Gallagher, a department spokesman, considered the fact that I am in what used to be known as “a family way,” he suggested that I not actually ride in a Rumbler-equipped squad car. “I don’t want you sitting in the back and going into childbirth,” he said. “I’m not handy with that.”
I’m not so handy with it either, so I rode in Officer Gallagher’s car while Officers Jeff Donato and Matthew Powlett of the 10th Precinct drove ahead of us, Rumbling as they went.
We zoomed up the Franklin D. Roosevelt Drive on what appeared to be the only day in recent history that it was free of traffic. When at last we did encounter at least a few other cars, the officers in the front car flipped on the Rumbler, switching among its sound effects: the wail, the yelp, the hi-lo, the fast stutter.
The Rumbler is no louder than a standard siren. In fact, it’s quieter — 10 decibels lower, which translates to only half the volume. But because low-frequency sound waves penetrate cars better than those at a higher pitch, drivers experience the Rumbler as much louder than a standard siren. That’s good news for pedestrians who might prefer not to be deafened, though not necessarily for the officers in Rumbler-equipped cars. To spare the officers’ ears, the device cuts off after eight seconds.
But the officers who demonstrated it for me said they had used it in repeated intervals for longer durations. And though Federal Signal describes the Rumbler as an “intersection-clearing device,” the officers also recounted using it while zipping up long stretches of highway. “It’s like the Red Sea parting,” Capt. Christopher Ikone said.
Low-frequency sound can have physical effects, like making you feel queasy. Enough, in fact, to be of interest to some weapons manufacturers, but their experiments take place at much lower frequencies and much higher amplification than the Rumbler employs. In fact, despite the siren’s name, the rumbling effect is subtle — far less than what you experience when an Escalade rolls up beside you at a stop light, tinted windows lowered, custom speakers blaring and thunder bass thumping. Hearing a Rumbler while standing on the street, I felt a slight tingle under my ribs; in Officer Gallagher’s car, I felt a gentle reverberation on the seat.
I can faithfully report that the Police Department’s newest and soon-to-be-ubiquitous emergency alert signal does not cause eyeglasses to sprout hairline cracks that branch out across the lens and hang there for one long moment before the entire thing shatters with a delicate “plink,” as in some Bugs Bunny cartoon. Nor does it reprogram the rhythm of your heartbeat, the way a loud song on the radio can make you completely forget what you’d been humming when you heard it. Nor does it induce premature labor in pregnant women. It may, however, have caused an innocent citizen heart palpitations.
As we zoomed back down the F.D.R. Drive, dual-tone sirens blaring so we could see the other cars scatter, the driver of a Toyota RAV4 apparently thought he was being singled out and pulled to a complete halt — in the left lane of the highway. That’s an unwise thing to do in any case; an extremely unwise thing to do when you’ve got a police cruiser right behind you.
If the driver did sustain any coronary distress from the incident, help was nearby: a Fire Department ambulance was driving just a bit farther south. As we passed, its siren let out a few warning bleats. But they were the old variety: one tone, no tingling. Compared with the basso profundo confidence of a Rumbler, it sounded like a jealous whine.
From Australia
WIND FARM NO-GO ZONES TO BE ESTABLISHED
SOURCE:ABC www.abc.net.au
August 29, 2011
By Anthony Stewart
The State Government is set to introduce new planning rules that will restrict where wind farms can be constructed.
Sweeping changes to the rules governing the construction of wind farms in Victoria will be gazetted today.
The Planning Minister, Matthew Guy, has amended local government planning schemes and state planning provisions that will deliver on a Coalition election promise to create wind farm no-go zones.
Wind farms will be prohibited in areas including along the Great Ocean Road, Mornington Peninsula, Macedon and Yarra Ranges and Wilsons Promontory.
The Government has formalised the set-back policy that stops the construction of wind turbines within two kilometres of houses, without the consent of the owner of the home.
The amendment also blocks the construction of wind turbines within five kilometres of major regional centres, a change that had not previously been flagged by the State Government.
Russell Marsh from the Clean Energy Council says the two kilometre setback policy will result in billions of dollars in lost investment
“The two kilometre setback the Government was talking about would reduce investment in wind energy in Victoria by 50 and 70 per cent,” he said.
“We were forecasting over $3 billion in investment will disappear from Victoria because of the two kilometre setback policy.”
The State Opposition’s planning spokesman, Brian Tee, says the Government has changed planning rules by stealth.
He says the Planning Minister should have introduced legislation if he wanted to block wind farm development.
“He absolutely should have brought this to the Parliament because this is going to have serious consequences,” he said.
“He hasn’t got the balance right and the cost is going to be paid by the environment.”
SECOND STORY:
SOURCE: The Washington Post, www.washingtonpost.com
August 28,2011
By Darryl Fears,
Six birds found dead recently in Southern California’s Tehachapi Mountains were majestic golden eagles. But some bird watchers say that in an area where dozens of wind turbines slice the air they were also sitting ducks.
The U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service is investigating to determine what killed the big raptors, and declined to divulge the conditions of the remains. But the likely cause of death is no mystery to wildlife biologists who say they were probably clipped by the blades of some of the 80 wind turbines at the three-year-old Pine Tree Wind Farm Project, operated by the Los Angeles Department of Water and Power.
As the Obama administration pushes to develop enough wind power to provide 20 percent of America’s energy by 2030, some bird advocates worry that the grim discovery of the eagles this month will be a far more common occurrence.
Windmills kill nearly half a million birds a year, according to a Fish and Wildlife estimate. The American Bird Conservancy projected that the number could more than double in 20 years if the administration realizes its goal for wind power.
The American Wind Energy Association, which represents the industry, disputes the conservancy’s projection, and also the current Fish and Wildlife count, saying the current bird kill is about 150,000 annually.
Over nearly 30 years, none of the nation’s 500 wind farms, where 35,000 wind turbines operate mostly on private land, have been prosecuted for killing birds, although long-standing laws protect eagles and a host of migrating birds.
If the ongoing investigation by the Fish and Wildlife Service’s law enforcement division results in a prosecution at Pine Tree, it will be a first. The conservancy wants stronger regulations and penalties for the wind industry, but the government has so far responded only with voluntary guidelines.
“It’s ridiculous. It’s voluntary,” said Robert Johns, a spokesman for the conservancy. “If you had voluntary guidelines for taxes, would you pay them?”
The government should provide more oversight and force operators of wind turbines to select sites where birds don’t often fly or hunt, the conservancy says. It also wants the wind industry to upgrade to energy-efficient turbines with blades that spin slower.
The lack of hard rules has caused some at the conservancy to speculate that federal authorities have decided that the killing of birds — including bald and golden eagles — is a price they are willing to pay to lower the nation’s carbon footprint with cleaner wind energy.
But federal officials, other wildlife groups and a wind-farm industry representative said the conservancy’s views are extreme. Wind farms currently kill far fewer birds than the estimated 100 million that fly into glass buildings, or up to 500 million killed yearly by cats. Power lines kill an estimated 10 million, and nearly 11 million are hit by automobiles, according to studies.
“The reality is that everything we do as human beings has an impact on the natural environment,” said John Anderson, director of siting policy for the wind-energy association.
Next Story
WIND POWER IS DYING
SOURCE: frontpagemag.com
August 28, 2011
By Tait Trussell,
While the U.S. is dumping billions of dollars into wind farms and onshore and offshore wind turbines, this energy source is being cast aside as a failure elsewhere in the world.
Some 410 federations and associations from 21 European countries, for example, have united against deployment of wind farms charging it is “degrading the quality of life.”
The European Platform Against Wind farms (EPAW) is demanding “a moratorium suspending all wind farm projects and a “complete assessment of the economic, social, and environmental impacts of wind farms in Europe.” The EPAW said it objects to industrial wind farms which “are spreading in a disorderly manner across Europe” under pressure from “financial and ideological lobby groups,” that are “degrading the quality of life living in their vicinity, affecting the health of many, devaluing people’s property and severely harming wildlife.” A petition for a moratorium has been sent to the European Commission and Parliament, said EPAW chairman J.L Butre.
France, earlier his year ran into opposition to its plan to build 3,000 megawatts (MW) of offshore wind turbines by 2020. That year is the target date the European Union set for providing 20 percent of its energy through renewable sources. An organization called the Sustainable Environment Association, opposes wind power, saying the subsidies will “not create a single job in France.”
In Canada, Wind Concerns Ontario (WCO) has launched a province-wide drive against wind power. It said Aug. 8 it wants to ensure that the next government is clear that “there is broad based community support for a moratorium…and stringent environmental protection of natural areas from industrial wind development.” WCO claimed, “The Wind industry is planning a high powered campaign to shut down support” for the WCO’s aims. “Our goal is to store the petition until the next legislative session gets underway in the fall…”
The Netherlands has approximately 2,000 onshore and offshore wind turbines. But even though Holland is synonymous with windmills, the installed capacity of wind turbines in the Netherlands at large has been stagnant for the past three years, according to an article in February in the Energy Collective. It was 2237 megawatts (MW) at the end of 2011. That was said to be about 3.37 percent of total annual electricity production. The principal reason for the stagnant onshore capacity “is the Dutch people’s opposition to the wind turbines.” They are up to 400 feet in height.
The Dutch national wind capacity factor is a dismal 0.186. The German wind capacity factor “is even more dismal at 0.167,” the article said.
Expanding wind power to meet the European Union’s 20 percent renewables target by 2020 meant adding at least another thousand 3 MW, 450-foot wind turbines to the Dutch landscape “at a cost of about $6 billion.” Not surprisingly, the Dutch people found that to be far too costly—“an intrusion into their lives and an unacceptable return on their investment, especially when considering the small quantity of CO2 reduction per invested dollar.”
An added 3,000 MW of offshore turbines also was rejected. The capital cost was figured at $10 to $12 billion. The cost was judged to be too much and the wind energy produced too little. “The energy would have to be sold at very high prices to make the project feasible.” The article added, “The proposed Cape Wind project in Massachusetts is a perfect example of such a project.” Environmental Lawyer Robert F. Kennedy, Jr. in July wrote an op-ed piece in the Wall Street Journal blasting the project off Cape Cod as “a rip-off.” Recently, the Netherlands became the first country to abandon the European Union target of producing 20 percent of its domestic power from renewables by 2020.
In Denmark, the Danes became aware that the poor economics of their heavily-subsidized wind energy is a major reason for the nation’s high residential electric rates. Opposition to the gigantic onshore turbines was so great that the state-owned utility finally announced last year that it would abandon plans for any new onshore wind facilities.
The Energy Collective article also reported that a CEPOS (Center for Political Studies) study found that 90 percent of wind energy sector jobs were transferred from other technology industries and that only 10 percent of the wind industry jobs were newly created jobs. As a result, the study said, Danish GDP is $270 million lower than it would have been without wind industry subsidies.
The Australian government, like the U.S., has placed a major emphasis on deploying renewable sources of energy, especially wind energy. As in the U.S., Australia set a target of 20 percent of its energy to come from renewal sources by 2020. The government provides generous subsidies and tax breaks to wind energy developers. But medical studies on farmer families living within 5 miles of wind farms found health problems ranging from sleep deprivation to nausea. Similar health effects have been discovered in other locations, including in the U.S.
Because wind blows only intermittently, Britain has determined that it will have to construct an additional 17 natural gas-powered plants as back-ups to wind to keep the lights on by 2020. These plants will cost 10 billion pounds, according to a posting by the Institute for Energy Research. One analyst was quoted as saying, “Government’s obsession with wind turbines is one of the greatest blunders of our time.”
Onshore wind power today costs about $0.13 per kWh. That’s nowhere near either the objective of the U.S. Department of Energy or the cost of competing power sources. The wind turbines jutting into the sky all across the country exist only because of the massive federal subsidies. Is this considered a failure by Obama officials? No way. Obama’s 2012 budget proposal increases renewables spending by 33 percent.
Wind farms in Texas that will cost $400 million over the next two years produce, incredibly, an average of only one job for every $1.6 million of capital investment. So the state’s comptroller general figured, according to a December 20, 2010 story in the Austin American-Statesman.
As long ago as 1973, then-President Nixon called for “Project Independence” in reaction to the OPEC oil embargo. The project was to achieve energy independence through development of alternative energy sources, such as wind, solar and geothermal power. So, there’s nothing new about renewable energy.
The Obama 2012 budget asks for $8 billion for “clean” energy, mainly wind power subsidies. As recently as Feb. 7, the secretaries of Energy and Interior announced plans to launch dozens of offshore turbines miles out at sea, while admitting the expense would be unknown. Despite generous subsidies, wind power is expected to provide no more than 8 percent of electric power in the U.S. by 2030.
The American Wind Industry Energy Association, the wind lobby group, said the top five states for wind energy were Texas, Iowa, California, Minnesota, and Washington. It said the second quarter of 2011 saw over 1,033 megawatts of capacity installed. It also maintained that wind is second only to natural gas and U.S. wind power represents more than 20 percent of the world’s wind power.
Over the next half century, say, it’s possible some new technologies will revolutionize energy. But, if so, they surely will come from the private sector — not government.